Outline
In this tutorial you will:
- Learn how to create a model composed of two parts, how to split it into two parts again and persist them with Spring Data CDO.
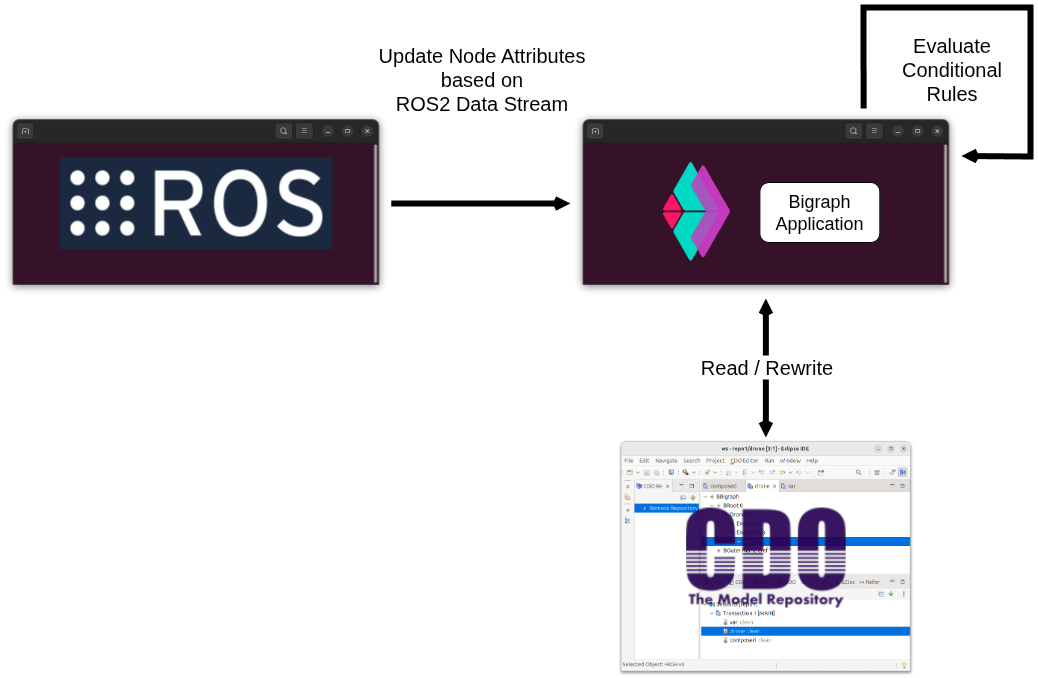
- Subscribe to a ROS2 topic in Java, and write an incoming data stream into bigraph node attributes.
- Define a conditional bigraph reaction rule that evaluates attributes and rewrites only the relevant part of the model.
The running example on the following pages models an agent (i.e., a drone) with an energy level that is updated based on a streamed integer value from ROS2 (e.g., /echo with std_msgs/Int16).
When the value is "low enough," a rule turns the agent’s energy marker from HIGH to LOW.
The complete example project can be found here: bigraphs-by-examples.streaming-bigraphs
Software Stack:
- Java 21 + Maven
- Bigraph Framework
- Spring Data CDO (w/ in-memory database)
- ROS2 Humble: rosbridge_suite for the rosbridge websocket server
Prerequisites
ROS2
ROS2 (Humble) and rosbridge websocket server running, for example:
# ROS 2 + rosbridge (example for Humble)
$ sudo apt install ros-humble-rosbridge-suite
$ source /opt/ros/humble/setup.bash
$ ros2 launch rosbridge_server rosbridge_websocket_launch.xml
Test publisher:
$ ros2 topic pub /echo std_msgs/Int16 "{data: 123}"
Eclipse CDO
This is where the bigraphical models are stored.
The actual implementation provides an in-memory CDO repository,
so you can experiment without setting up a full database.
See the class CDOStandaloneServerTest for details.
To start the in-memory CDO database (non-persistent storage):
$ mvn test -DrunDisabledTests=true -Dtest="CDOStandaloneServerTest#run_server_test_01"
You can also run this method directly from your IDE, such as Eclipse, IntelliJ IDEA, or VSCode.